Lecture 36
GUIs with tkinter
MCS 260 Fall 2021
Emily Dumas
Reminders
GUIs
Today we'll talk about making programs with graphical user interfaces (GUIs). How to do this?
Increasingly popular: Write a program accessed through a browser. HTML allows buttons, text entry boxes, drawing, etc..
Today: We'll build a GUI without a browser, using a toolkit, a library of functions for creating GUIs.
Tk and tkinter
Tk is a cross-platform GUI toolkit originally created for the TCL programming language.
tkinter is the Python module providing an interface to Tk. It is the only GUI toolkit in the standard library.
tkinter dates from the mid-1990s and shows it age in some ways.
Why learn tkinter?
There are many GUI toolkits, but many are:
- Platform-specific (Cocoa, WPF, ...) and/or
- Large and complex to install (GTK, Qt, Wx) and/or
- Proprietary
While tkinter is not common for new projects, it is similar enough to other toolkits to make it useful to learn.
Widgets
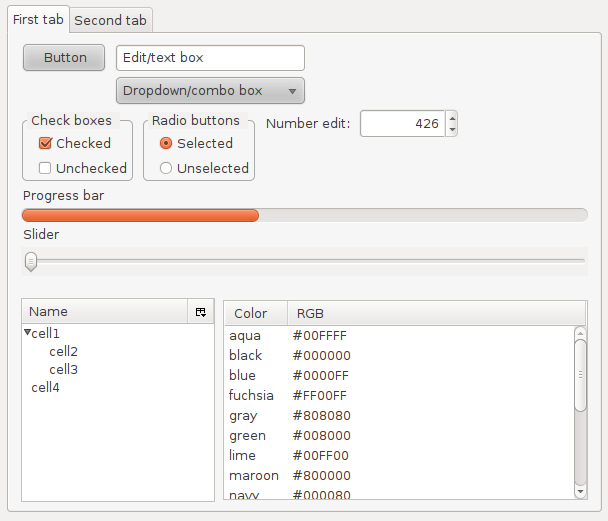
Widgets are standardized components of a GUI.
Basic GUI workflow
Create a window and hierarchy of widgets (buttons, sliders, etc.).
Specify functions to be called when user interacts with widgets, or in response to other events.
Start the GUI main loop, which never returns.
Key point: You lose control of what happens next. The program can only respond to things that happen in the GUI.
tkinter widgets
Module tkinter contains window setup functions, lots of constants, and misc. other stuff.
Module tkinter.ttk contains widgets for button, checkbox, text entry box, text label, drop-down menu, scrollbar, radio button (mutually exclusive choice), slider, etc.
Example
Let's build a simple GUI application that shows a text label and buttons to:
- Display some text in the label area
- Clear the text
- Quit
We'll use the tkinter module docs, the TkDocs tutorial, and the Unofficial reference manual by John Shipman.
Review
General pattern:
- Make a
tkinter.Tk - Make widgets (parent is the
tkinter.Tkor other widget) - Pack the widgets, or perform layout in another way
- Call
Tk.mainloop()
Widgets used today
tkinter.ttk.Button— activate to perform an actiontkinter.ttk.Label— displays text, not directly editable
References
- Official tkinter documentation
- The Tk docs tutorial demonstrates lots of features, and shows Python code for all its examples.
- Unofficial reference manual by John Shipman
Revision history
- 2021-11-15 Initial publication