MCS 275 Spring 2024 Worksheet 1¶
- Course instructor: Emily Dumas
Topics¶
This worksheet covers some initial setup and installation of software, followed by some coding exercises that use material from prerequisite courses.
Instructions¶
- This isn't collected or graded. Work on it during your lab on Jan 9 or Jan 11.
- If you took MCS 260 recently you may have some or all of the necessary tools installed already. That's fine. Be sure to test them out as outlined below and read through the worksheet to be sure you know what is assumed from now on.
Part I: Setting up a development enviroment¶
The tasks in this part of the worksheet expand on the Getting Started steps listed in the course web page.
If you plan to use your own computer to complete MCS 275 work, you need to make sure some things are installed and that you know how to use them.
If you plan to use UIC lab computers to do all of your work, the necessary software should already be installed there (allowing you to skip steps 1 and 4).
1. Install Python¶
You'll need Python 3, version 3.10 or higher, installed on your computer to develop code for MCS 275. The recommended method of installation depends on your platform:
- Windows: Install from the Microsoft Store (https://apps.microsoft.com/store/detail/python-310/9PJPW5LDXLZ5)
- MacOS: Most likely, Python 3 will be pre-installed, but it may be an older version. Check by running the command
python3in a terminal. If it is not already installed, or if the version is too old, we recommend installing it using either Homebrew or using the installer from python.org:- MacOS option 1: Homebrew-based install instructions https://docs.python-guide.org/starting/install3/osx/
- MacOS option 2: Python.org packages: https://www.python.org/downloads/macos/
- Linux: It is probably pre-installed. If not, use your distribution package manager to find and install the latest version of Python 3, and confirm that it is version 3.10 or higher. If you're using Linux and not sure how to install software or find your distribution package manager, ask for help.
2. Open a terminal¶
We'll do almost everything in MCS 275 using a text- and keyboard-based interface to your operating system. This takes the form of a terminal. The exact name will depend on your operating system. Test that you can find and open this program on your computer:
- Windows: The terminal we support for MCS 275 is Windows Terminal (available for free from the Microsoft Store) and among the various command interpreters it supports, you always want to select Powershell.
- MacOS: The terminal application is simply called Terminal, and is installed by default.
- Linux: The name and method of starting a terminal application depends on the distribution. In Ubuntu, the application menu will contain an entry simply called Terminal.
Once you have a terminal open, check that you can list the files in the current directory with the command
lsRetrieve the name of the current directory with the command
pwdYou can change to a new directory using the command
cd NEWDIRECTORYreplacing NEWDIRECTORY with the relative path or full path of the directory you want to move to. Typically, you'll want to move to the directory containing your Python programs as a first step in any work session.
(The terminal commands supported by Linux, MacOS, and Windows Powershell are actually quite different, but for the most part we'll stick to commands that work nearly the same way in all three of them.)
If you'd like a more detailed review of how files, paths, and directories work, check out these slides from the first lab in MCS 260:
3. Determine your interpreter name¶
Now that you know how to start a terminal, you need to determine how to start Python 3 (version 3.10 or later), which you have installed at this point, from within the terminal.
Most likely, the command will just be
python3But in some cases you may find that Python 3.10+ is installed but the command to open it is just called
pythonbut it's more likely that this command will start a different programming language (Python 2). It's important to look at what is printed when you run the command and find the one that opens Python 3. Here is what it looked like in virtual lab last year (when they still had Python 3.9):
PS C:\windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0> python
Python 3.9.1 (tags/v3.9.1:1e5d33e, Dec 7 2020, 17:08:21) [MSC v.1927 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>The >>> prompt tells you that you're still in Python, and it's waiting for you to type a line of code that will be executed immediately. You probably want to just quit Python and go back to the terminal, which you can do by entering
exit()at the >>> prompt and pressing Enter.
The command you use to run Python 3 is your interpreter name. Make note of it, because you'll use it a lot. Since it will be different for each student, the instructions for subsequent tasks require you to know your interpreter name. That is, any time you see python or python3 appearing in a command that a worksheet suggests you run, you will need to replace it with your interpreter name.
4. Install Microsoft VS Code¶
You'll need a programming text editor to work on MCS 275 assignments. The one we support directly in the course, and which we ask everyone to install, is
This is a free program available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux.
Install it using the instructions at the link above.
(It should already be installed in the Virtual Computer Lab.)
After installing it, figure out how to start VS code, for example by using an icon on the desktop, the start menu, or whatever method your operating system uses to launch applications.
5. Write a short program in VS code¶
Create a new file in VS code and paste the following text into it:
print("Hello world!")
x = 2**2024
print("2 raised to the power 2024 is equal to",x)Save it with a filename hello.py. When you save it, make note of where it ends up. On Windows or MacOS, the default save location may be the Desktop, or the Documents folder. Or you can use the save dialog box to select a different destination (e.g. a directory you make for the purpose of storing your MCS 275 work).
After you've saved the file, you can get a definitive answer about exactly where the file is stored on your computer as follows: Right-click on the filename tab in the VS code window, and select "Copy path" from the menu that pops up. Now, you can paste (Control-V) the filename into another application, such as the terminal. Try this. The filename might look something like
C:\Users\ddumas\Desktop\hello.pyon Windows, or
/home/ddumas/Desktop/hello.pyon Linux. The key point is that it shows the full name of the directory (e.g. C:\Users\ddumas\Desktop\) that contains the file. When you're working in the terminal, you will usually need to know the full name of the directory containing any files you want to use. Often, you'll want to cd to that directory to avoid typing the directory name each time you want to refer to a file.
6. Run your program in the terminal¶
VS code may show you a button that can run a Python program; it's a green triangle in the upper right corner. Please, please, PLEASE don't use that button. If you do, it will work sometimes but fail in confusing ways at other times, because VS code runs your program with the working directory set to a different directory than the one that contains the source code. We'll also write a lot of programs that deal with command line arguments, which can't be run using that button.
Open the terminal and change the working directory to the one containing the file hello.py you created in task 5. The cd command is used to do this. For example, on my Windows computer, the command to change directory is
cd C:\Users\ddumas\Desktopwhile on my Linux laptop it is instead
cd /home/ddumas/desktopIn general, the directory will be the initial part of the full path you get from VS code's "Copy path" menu option, all the way up to the last "/" or "\" that appears in the path.
- Potential "gotcha": If the name of a file or directory contains spaces, you need to put the entire thing in quotation marks to use it with a command in the terminal, e.g.
cd C:\Users\ddumas\Desktop\MCS260 # ok cd C:\Users\ddumas\Desktop\MCS 260 # NOT OK because of the space cd "C:\Users\ddumas\Desktop\MCS 260" # ok
Confirm that you're in the right directory by asking for a list of files. The terminal command for this is
lsYou should see hello.py in the output of that command.
Once you're in the right directory, run the script hello.py using a command that consists of the interpreter name followed by the filename hello.py. That means it will probably be one of these:
python3 hello.py
python hello.pyIf this works, you should see output similar to
Hello world!
2 raised to the power 2024 is equal to 19262436670846347392031476908129425025250972908565690536576715366557034932892257507560969240381070055776070333076654684242081379384095025715284438363580872488397882799685595090240357965463192526576553367605249624417300354625356052018307503663585287613023308427355471278958067829335371141795845269634682169867702921265166009915283307305910926756177053472594214712427738701898471231882846542686378117122755716279711487125433598373888940305889633836986838348646931190030053666061651831701491535739261700790928925621900974473384617130966781758198455075257681212153197607656258109000515030983061878796551140314972167. Download and run the "python checkup" script¶
Now that you have your development environment set up, let's run a script that checks to make sure your Python version is as expected (3.10+) and that your process of running scripts in the terminal works. Download this Python script and save it somewhere that you can find in the terminal:
Now, open a terminal, cd to the directory containing checkup.py, and then run that script. (Perhaps you want to open it in VS code and take a look before running it. That's generally a good practice.)
After you've changed directory, the command to run the checkup script will probably be one of these:
python3 checkup.py
python checkup.pyThe script will print a bunch of messages to the terminal, and may give WARNING: or ERROR: messages if something looks wrong. It will also try to display some emoji, shaded rectangles, and colored text, to check if your terminal supports these. Here's what the output looks like on my linux computer:
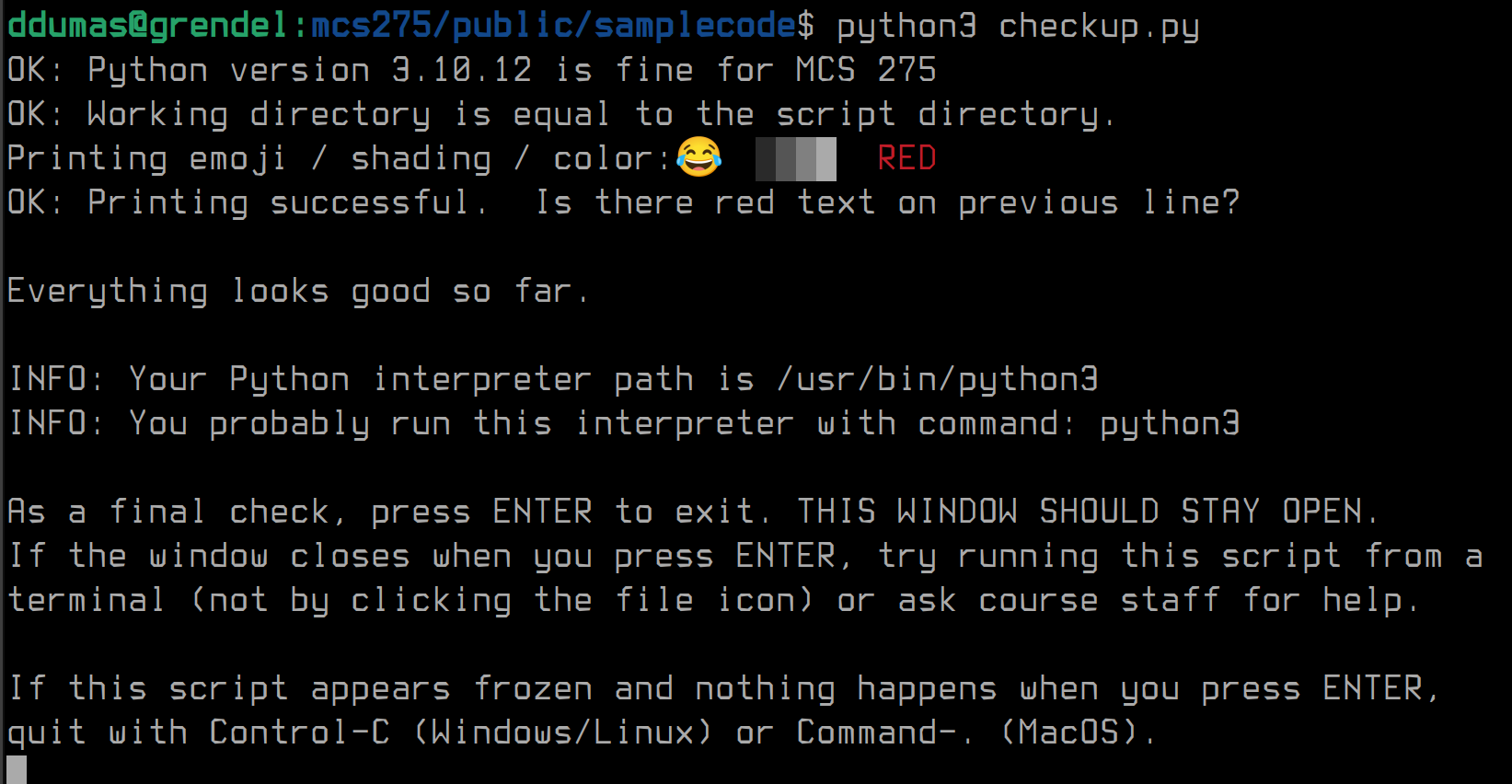
If the script shows any warnings or errors, try to fix the issues using the suggestions printed to the terminal in consultation with your TA.
Part II: Python Calisthenics¶
This section gives a series of exercises in which you'll write programs that are based on things you are expected to have seen in a prerequisite course. We'll talk about these in Lectures 2-3 as well, and the first quiz will cover the same kind of review material.
These start very easy and build up.
8. Squares¶
Create a simple program squares.py that prints the squares of the first 10 positive integers, so its output should look like
1
4
9
...
100Then, add a feature to this program where it accepts an optional command line argument which is the largest integer whose square should be printed (while 10 remains the default if no argument is given). Recall that command line arguments appear in the list sys.argv which is accessible after you import the sys module, and the items in this list are strings. So sys.argv[1] would be a string containing the first word or number on the command line after the name of the script.
Thus, for example, if you run the modified script as
python3 squares.py 3then it would be expected to produce the output
1
4
99. Getting to know our coding standards¶
Now that you've written a simple program from scratch, and have a full Python setup working, it's time to get acquainted with some code style rules.
All code you submit for credit needs to follow the rules described in the
These rules enforce good coding practices and ensure your programs are readable to both humans and computers.
Read the list of rules now. If any of the rules seem unclear on a first reading, check the section later in the document that gives examples of compliant and non-compliant code for that rule.
Then, take the program below (which works!) and fix it so that it does the same thing but complies with the MCS 275 rules. (Note: The rules say you need to add a declaration stating that the program is your own work, or that it is derived solely from a template provided by the instructor. That's because all graded work in MCS 275 is done individually. Since this is a worksheet, collaboration is allowed and if you work with others you should instead list your collaborators.)
# I am a program that doesn't follow MCS 275 coding guidelines
# Please fix me.
def thing(x):
return "{} is one greater than {}".format(x,x-1)
def thing2(x):
return "{} is one less than {}".format(x,x+1)
s = str(input("Please enter your name"))
print("Hello",s,", this is a sample Python program.")
ss = list(range(5))
sss = [ x+5 for x in ss ]
ssss = [ 10*x for x in sss ]
for i in range(len(ssss)):
sssss = 'Some things that are true:\n' + thing(ssss[i]) + "\n" + thing2(ssss[i]) + '\n\n'
print(sssss)10. Thinking inside the box¶
One of the nice things about Python is that strings can contain any Unicode character (as opposed to strings in some other programming languages where the set of available characters is much more limited).
Some Unicode characters are made for drawing "text graphics" boxes, like this:
╔══════════╗
║ Look, ║
║ a box! ║
╚══════════╝The box drawing characters used above are:
\u2550or═\u2551or║\u2554or╔\u2557or╗\u255aor╚\u255dor╝
Write a program box.py that prints a unicode text box of specified width and height. It should expect at least two command line arguments, giving the width and height of the box. If only those are given, the box should be printed to the screen. If a third argument is given, it should be a filename and the box should be written to that text file instead of being printed to the screen.
So, for example, the command
python box.py 3 4should result the following text being printed, exactly:
╔═╗
║ ║
║ ║
╚═╝(This box has a width of 3 characters and a height of 4 lines). Similarly, the command
python box.py 12 2 box.txtshould not print anything to the screen, but should result in a file box.txt being created that contains the following text, exactly:
╔══════════╗
╚══════════╝Recommended structure of your program:
There are at most three different lines of text that appear in a box: The top of the box, the line that repeats some number of times to make the vertical sides of the box, and the bottom of the box.
I suggest you generate these three lines and store them in strings, and then assemble them into one bigger string that has all the lines and line breaks (\n characters) that you need.
To generate the strings, you can use the fact that multiplication of a string by an integer will repeat the string a certain number of times. For example, "foo"*3 evaluates to "foofoofoo".
It would be a good idea to put the part of the program that writes the box to a file into a function and have the rest of the program create a string that contains the box. Then you can decide whether to print the string or call the function to write it to a file based on whether there is a third command line argument.
Bonus round¶
Work on this more challenging exercise if you finish the rest of the worksheet before discussion ends. The solutions to the worksheet won't include solutions for the bonus problem, but it's still good practice!
11. Digits to word lengths¶
Consider this process: Start with a positive integer like
2781
Write out each digit as an english word:
two, seven, eight, one
Then replace each word with its number of letters (e.g. "two" has 3 letters, "seven" as 5, etc.):
3 5 5 3
Use these numbers as digits of a new integer
3553
Finally, take the average of the new integer and the old one, and if the result is not an integer, round it down to the nearest integer:
(2781 + 3553) // 2 = 3167 (no rounding happened in this case)
(Why are there two slashes there? That's how you perform integer division.)
Write a Python function dwl(n) that takes an integer n and returns the integer that results from this process. So, for example we have:
dwl(2781)
Now, consider what happens when you apply this function over and over again, e.g. start with n, compute dwl(n), then dwl(dwl(n)), then dwl(dwl(dwl(n))), etc., to get a sequence. For 2781 this sequence looks
like:
2781, 3167, 4251, 4297, 4321, 4427, 4431, 4442, 4442, 4442, 4442, ...
It continues with 4442 repeating forever.
That's what happened when starting with 2781, but what happens when you do the same thing but start with a different value of n, like 7847? Does it always seem to end up repeating some number over and over again?
Write a program to explore this more systematically, for example by searching for a repeating pattern (or lack thereof) for every 4-digit starting number.