Lecture 12
Divide and Conquer
Mergesort
MCS 275 Spring 2024
Emily Dumas
Lecture 12: Mergesort
Reminders and announcements:
- Project 1 due 11:59pm Friday
- Project 1 autograder is open
- Please tell me if you have any trouble interpreting the report or if you think it is wrong.
- Worksheet 5 posted; lab 5 should allow time to ask TA project questions
Divide and conquer
A strategy that often involves recursion.
- Split a problem into parts.
- Solve for each part.
- Merge the partial solutions into a solution of the original problem.
Not always possible or a good idea. It only works if merging partial solutions is easier than solving the entire problem.
Decrease and conquer
Divide and conquer
Comparison sort
Problem: A list of length n is given. For any two elements you are allowed to ask which one is "smaller". Using this information, put the list in increasing order.
Mergesort
A divide-and-conquer solution to comparison sort.
Fast, often used in practice.
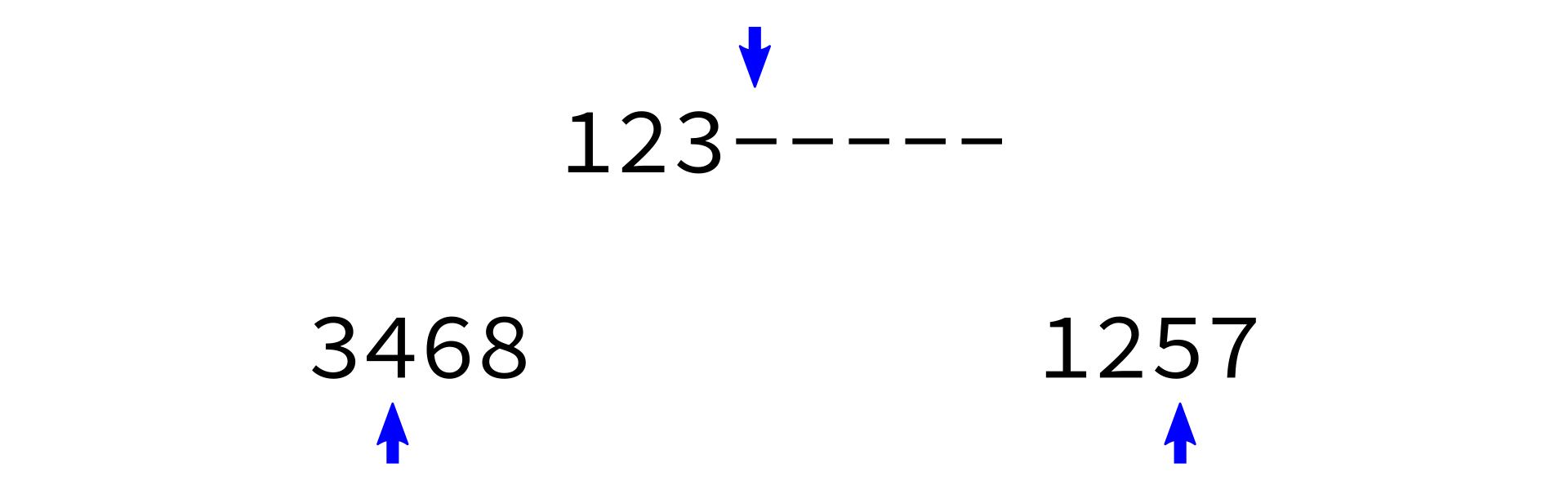
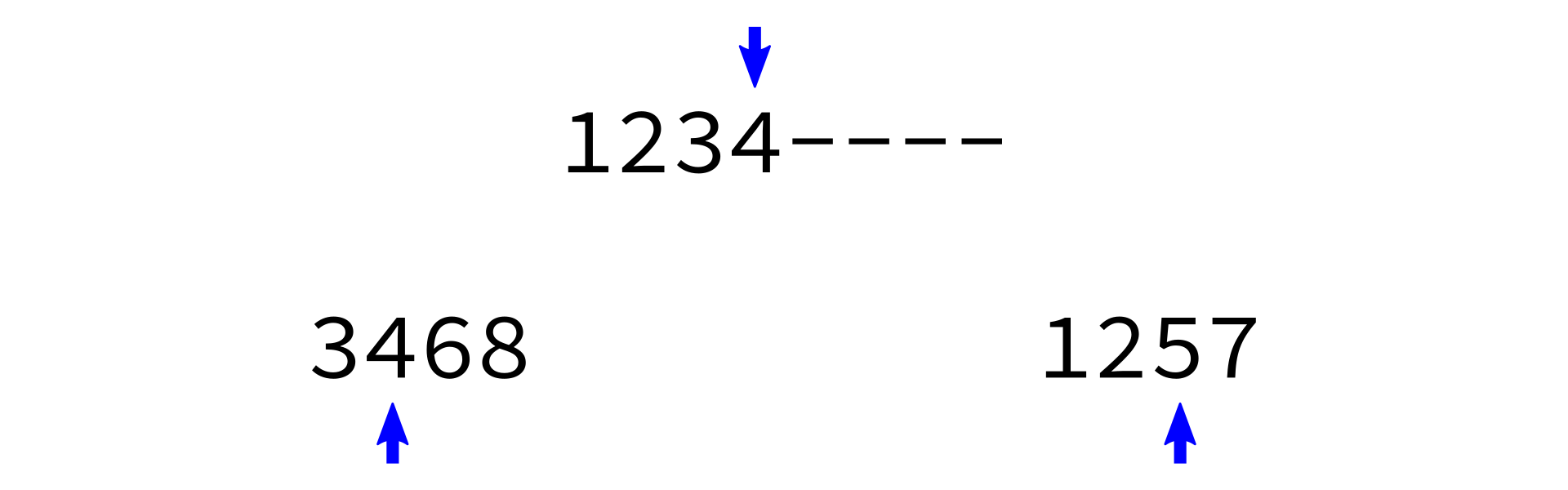
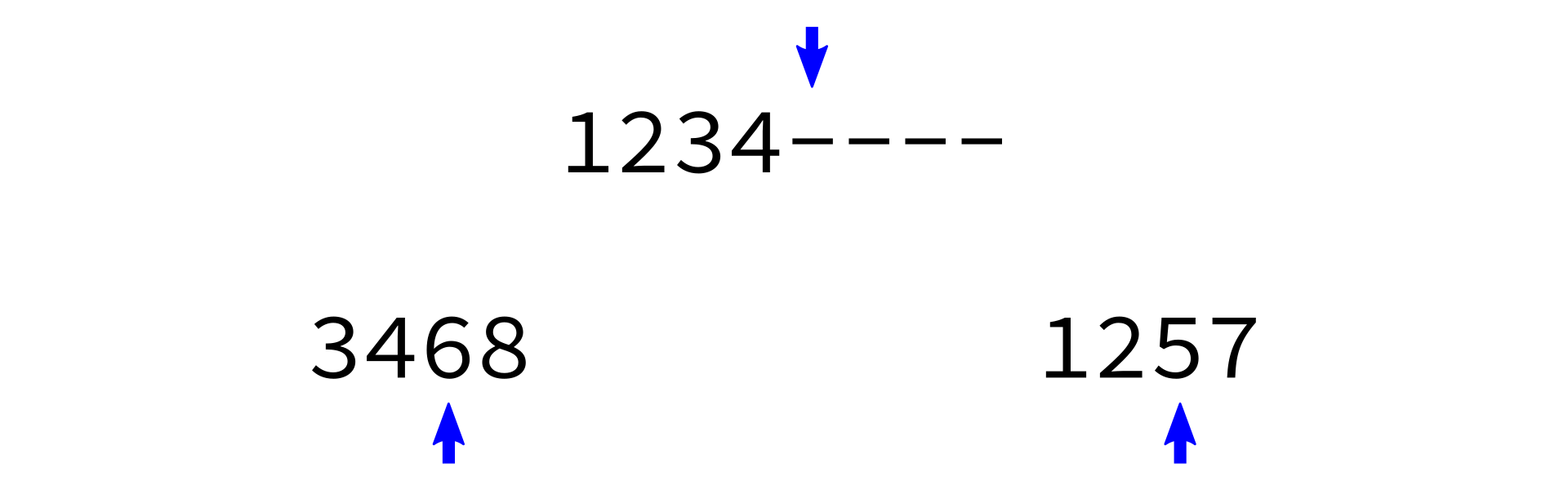
Key: Two sorted lists can be easily merged into one sorted list.
mergesort:
Input: list L whose elements support comparison.
Goal: return a list that contains the items from L but in sorted order.
- If
Lhas 0 or 1 elements, returnL - Otherwise, divide
Linto rougly equal piecesL0andL1. - Recursively call
mergesortonL0andL1. - Use
mergeto merge these sorted lists and return the result.
Mergesort example

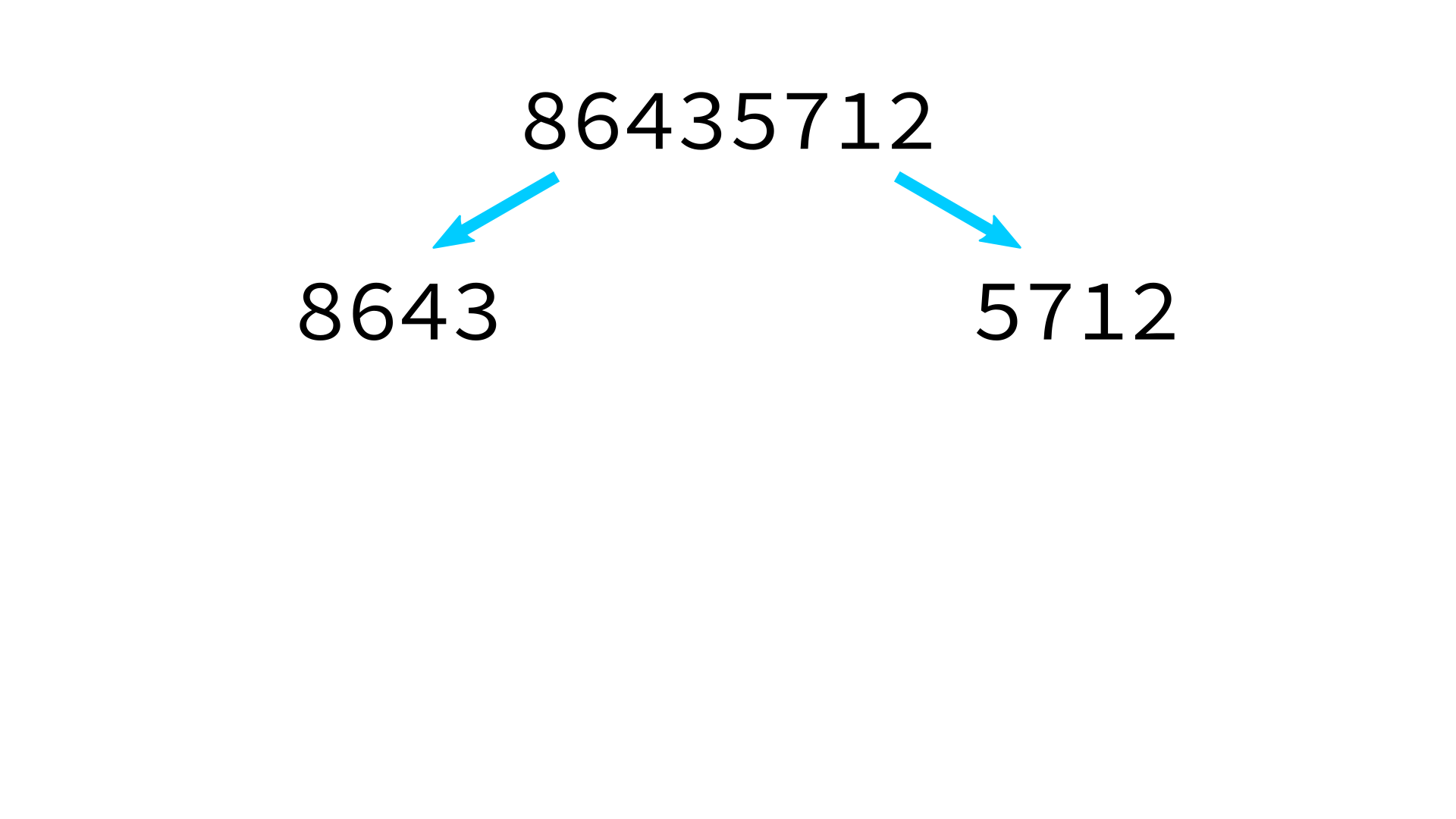
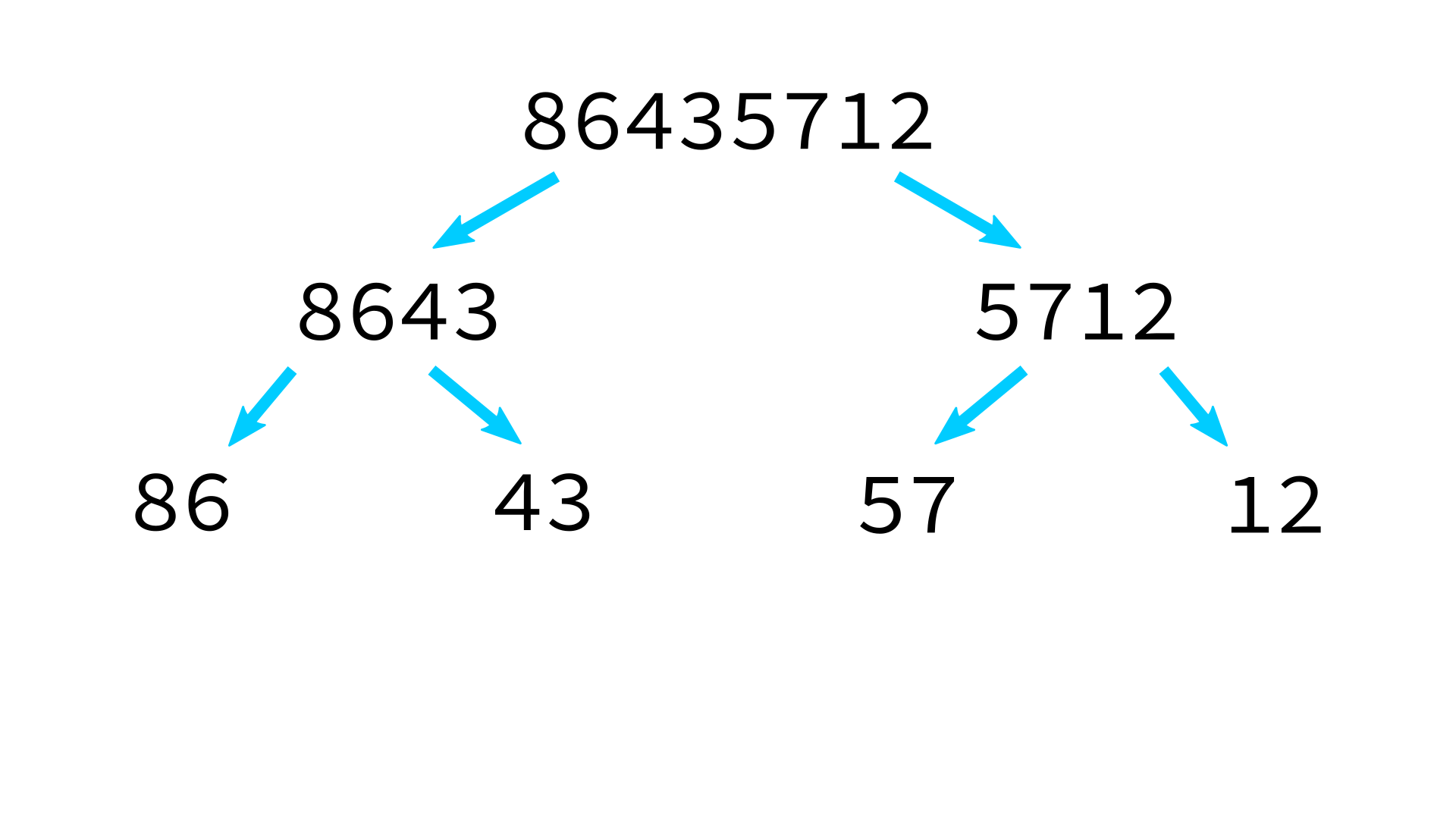
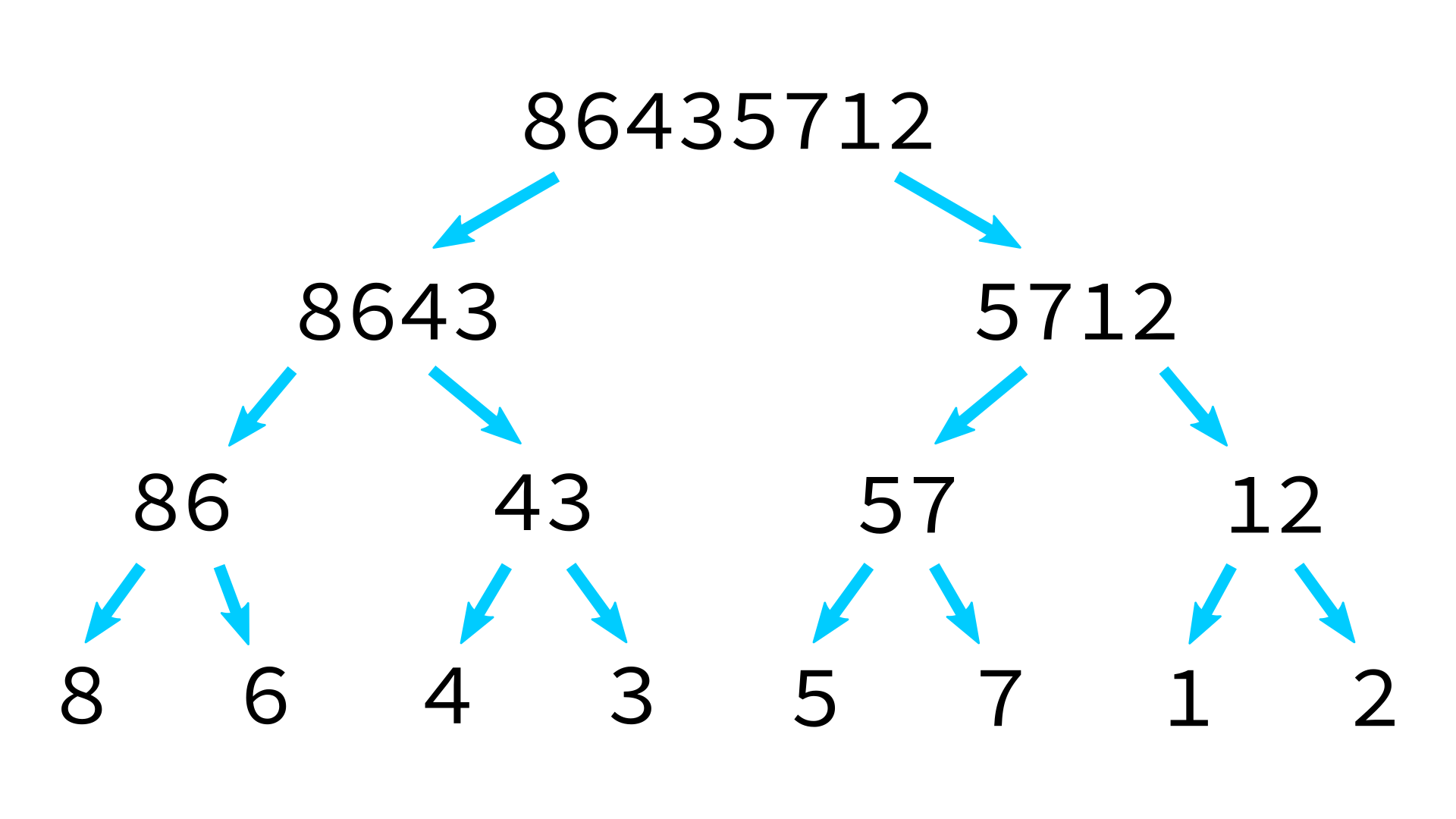
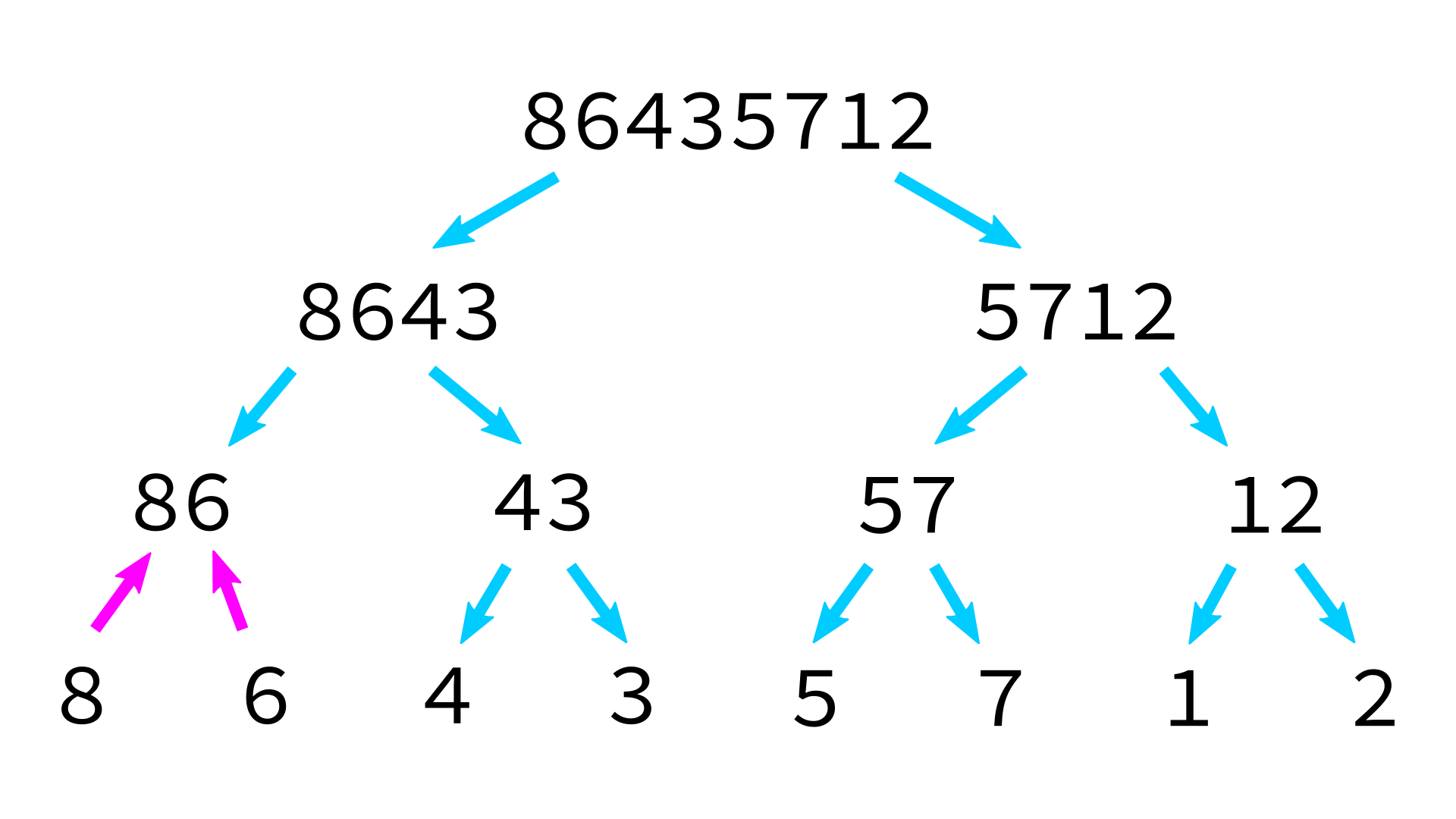
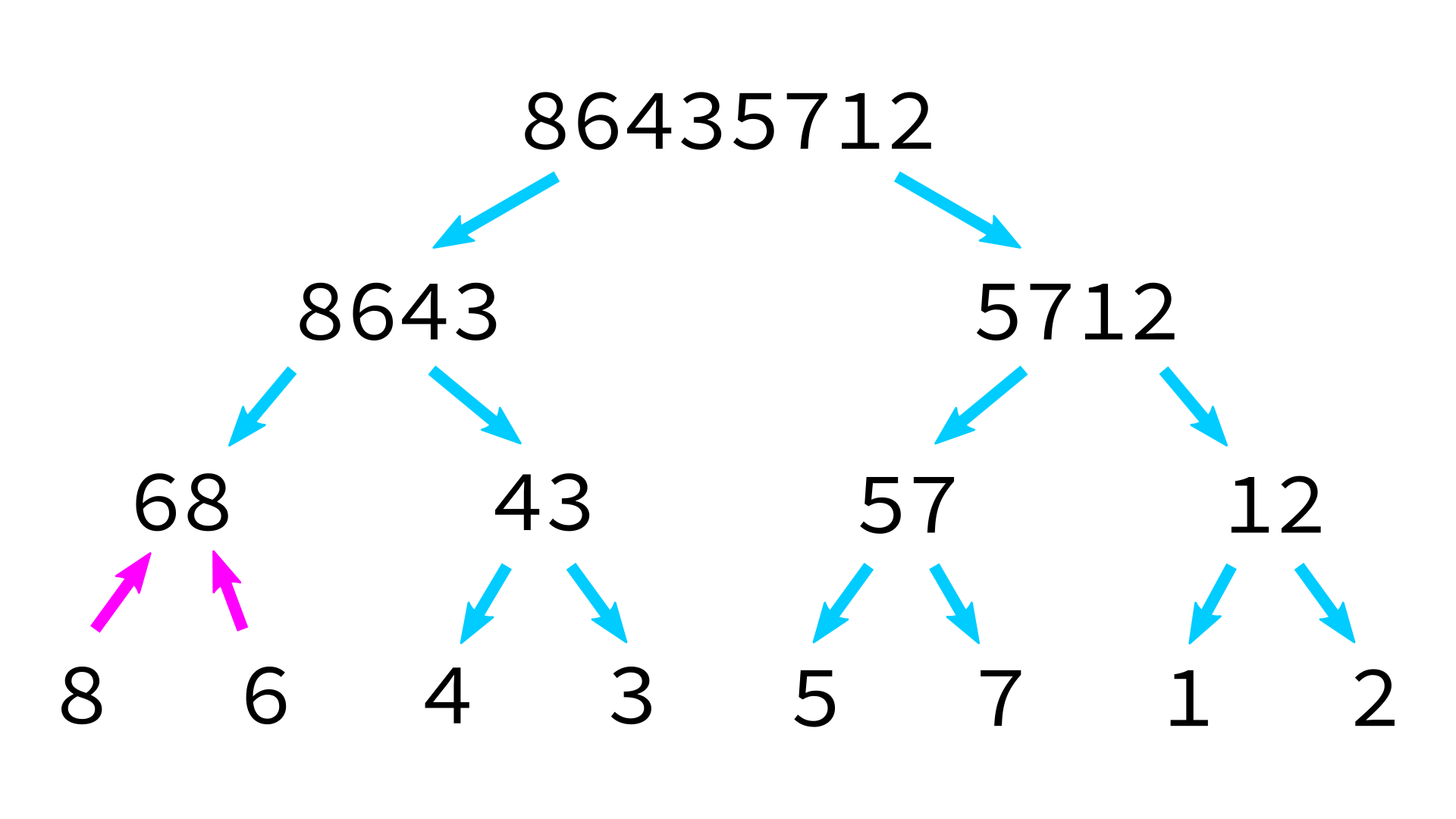
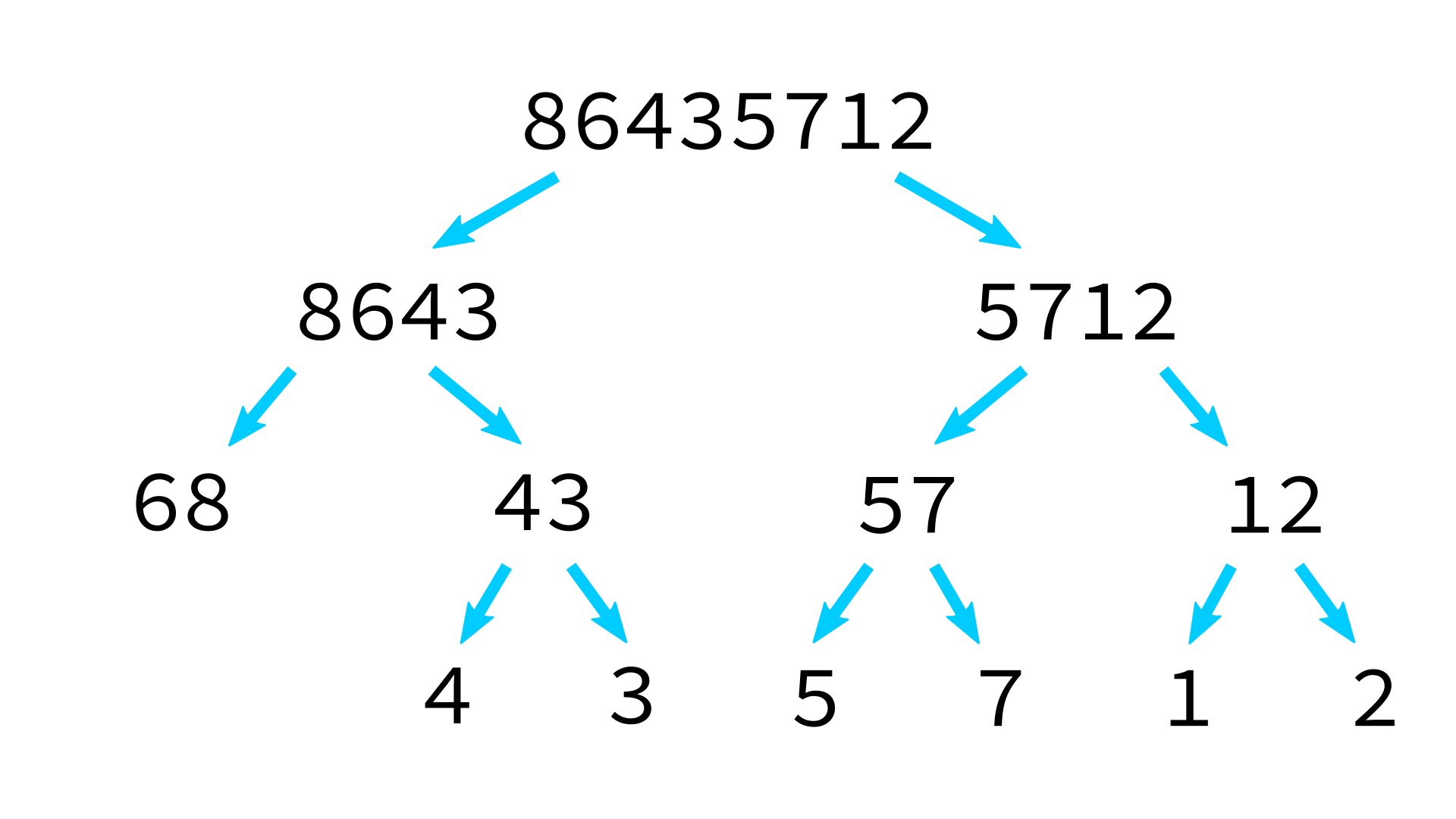
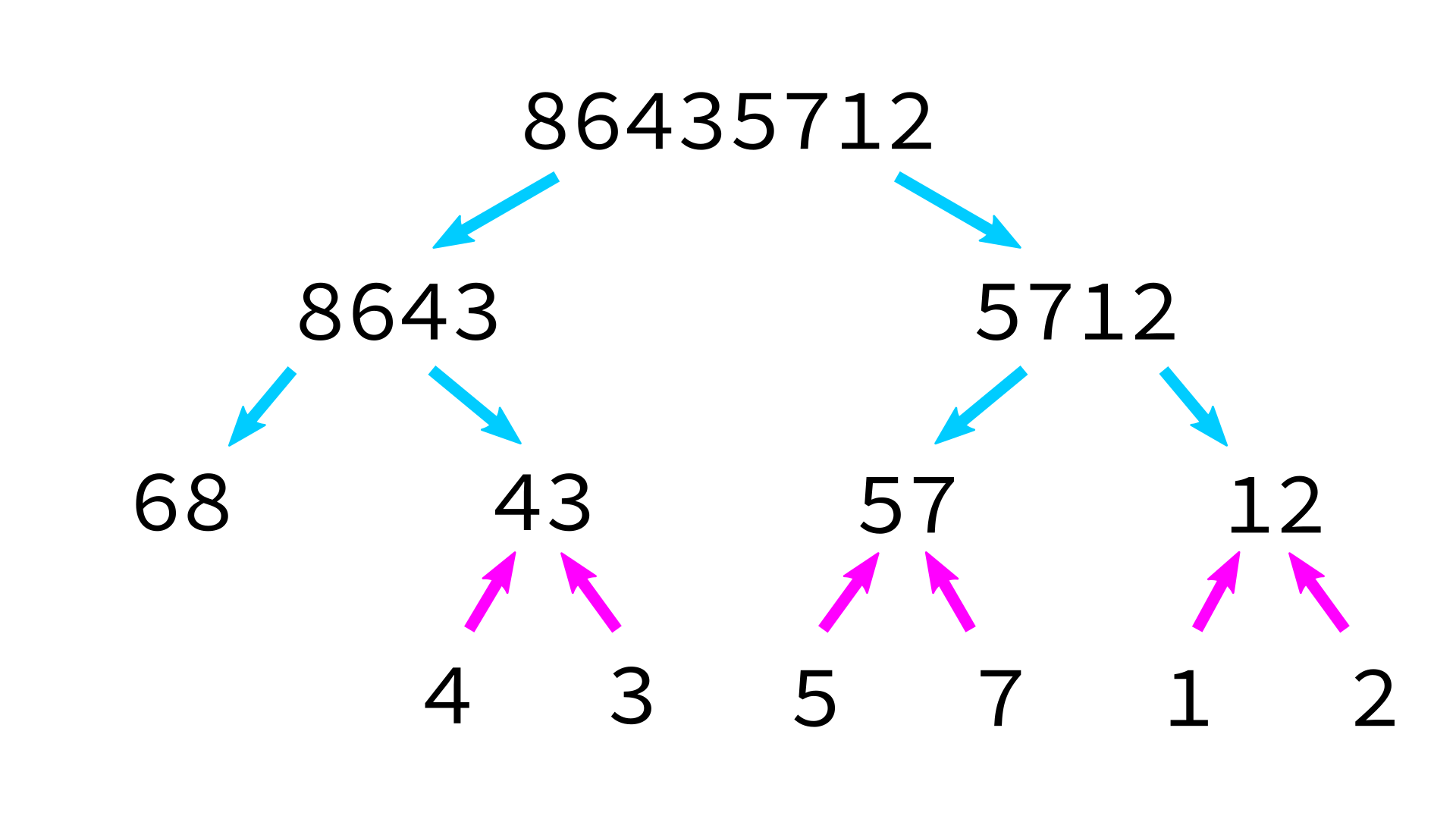
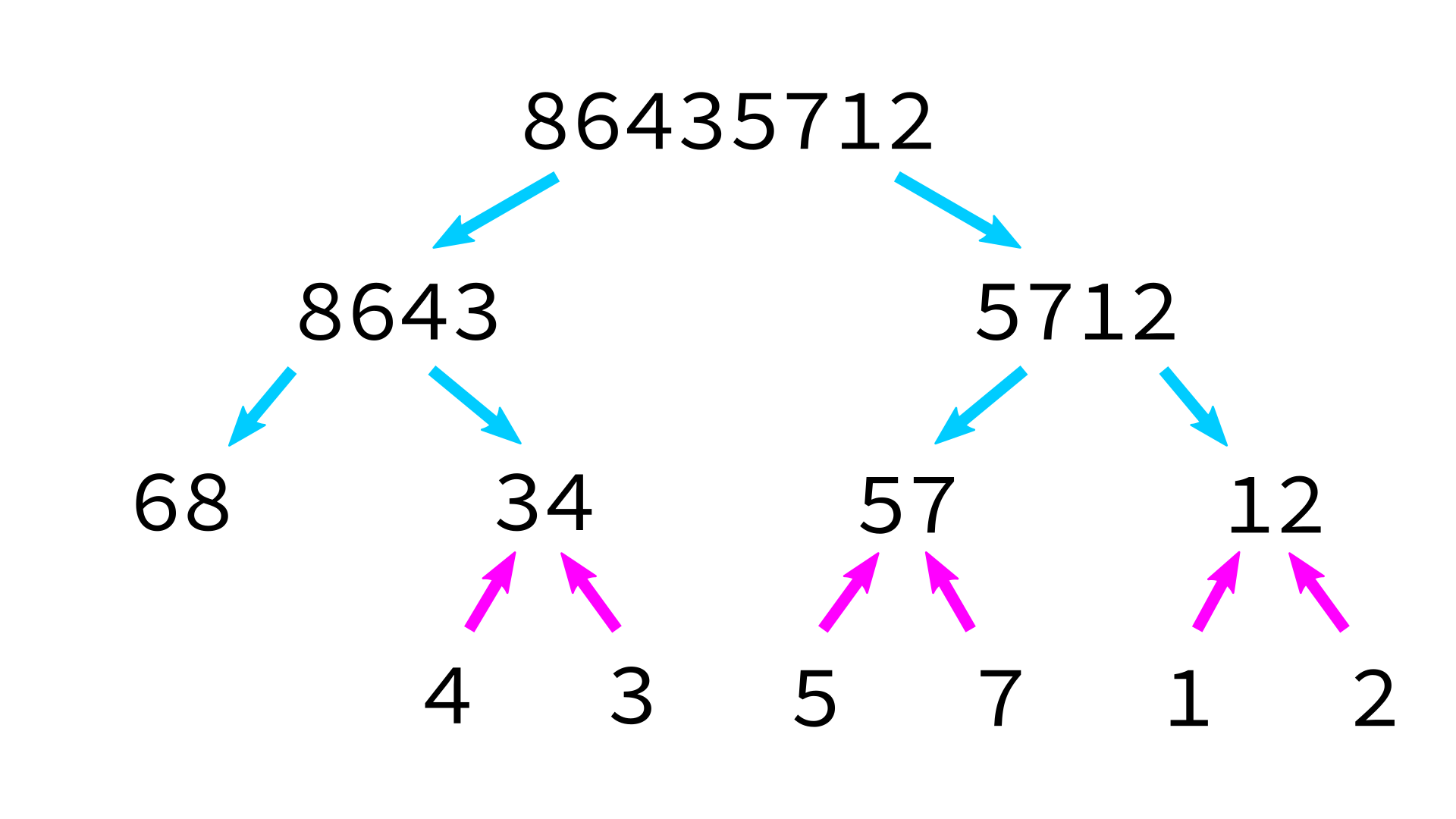
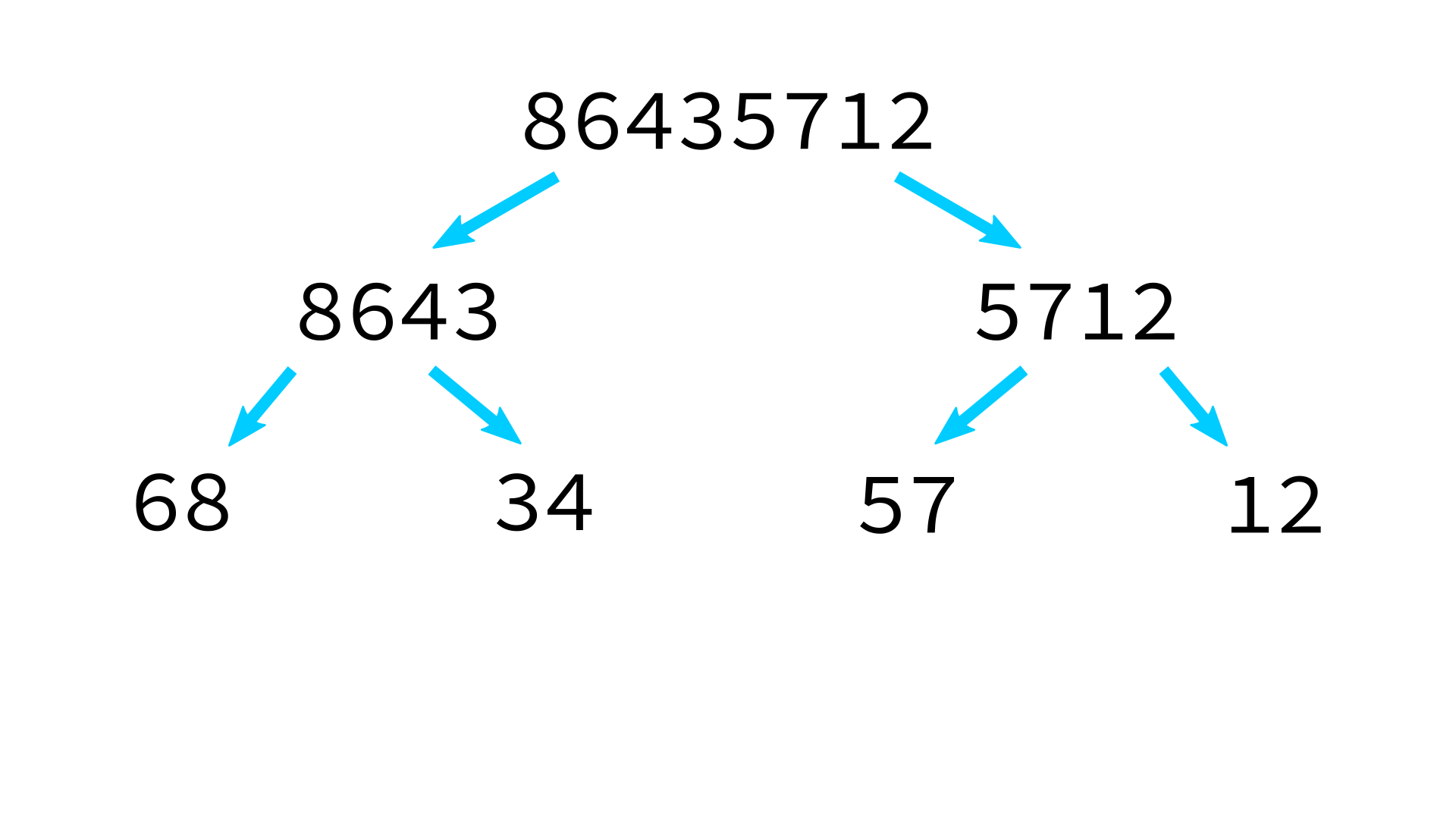
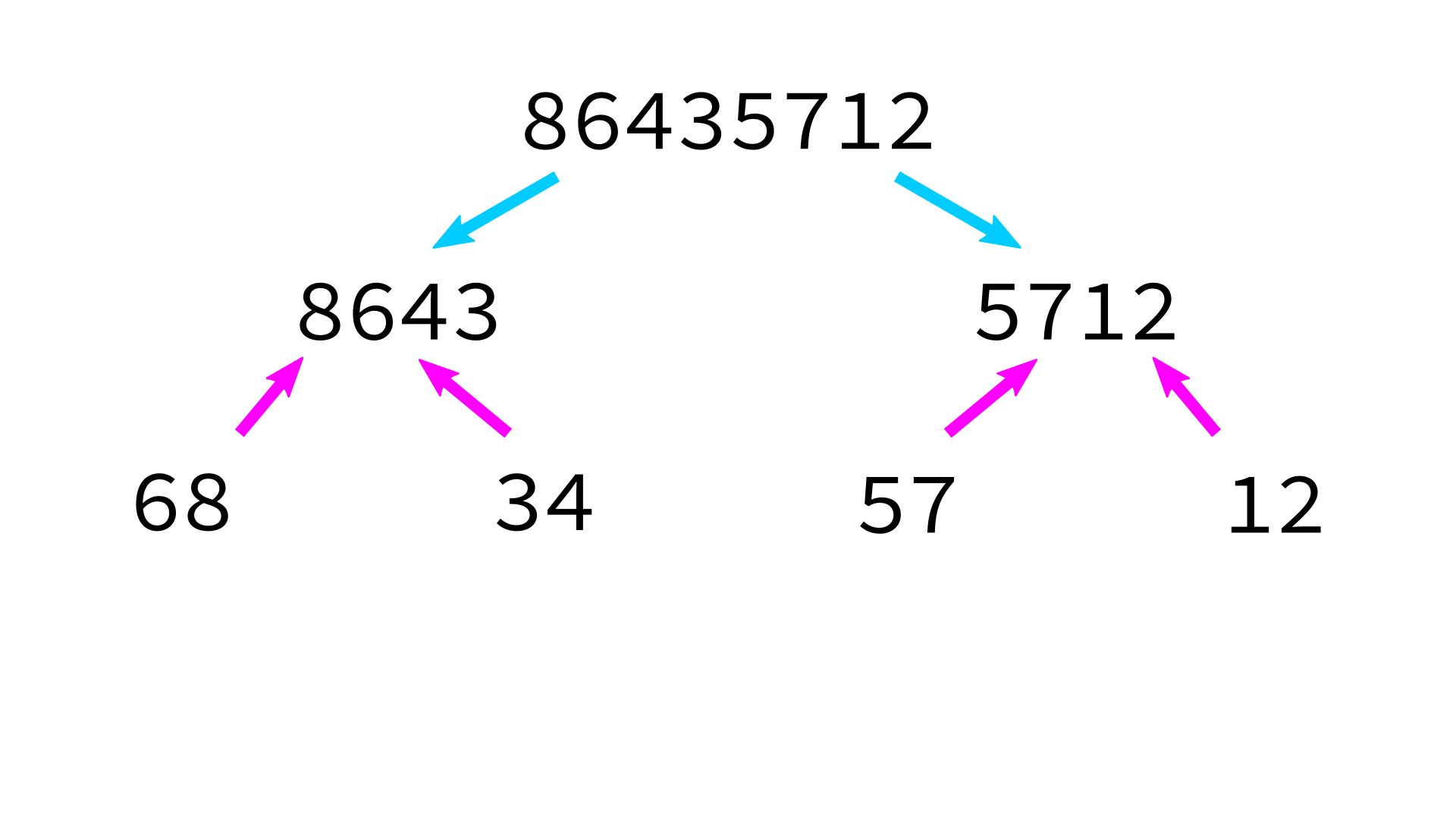
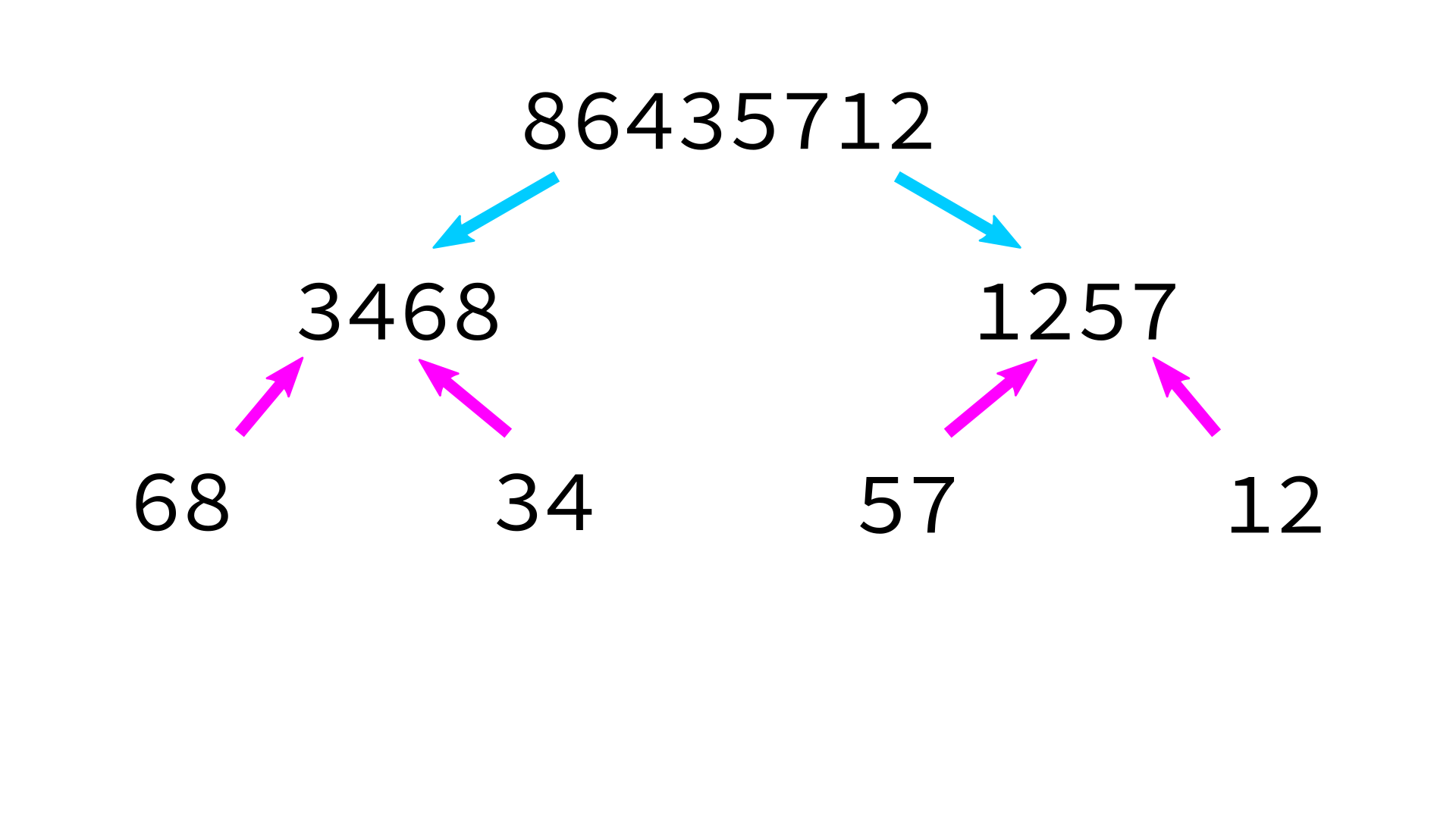
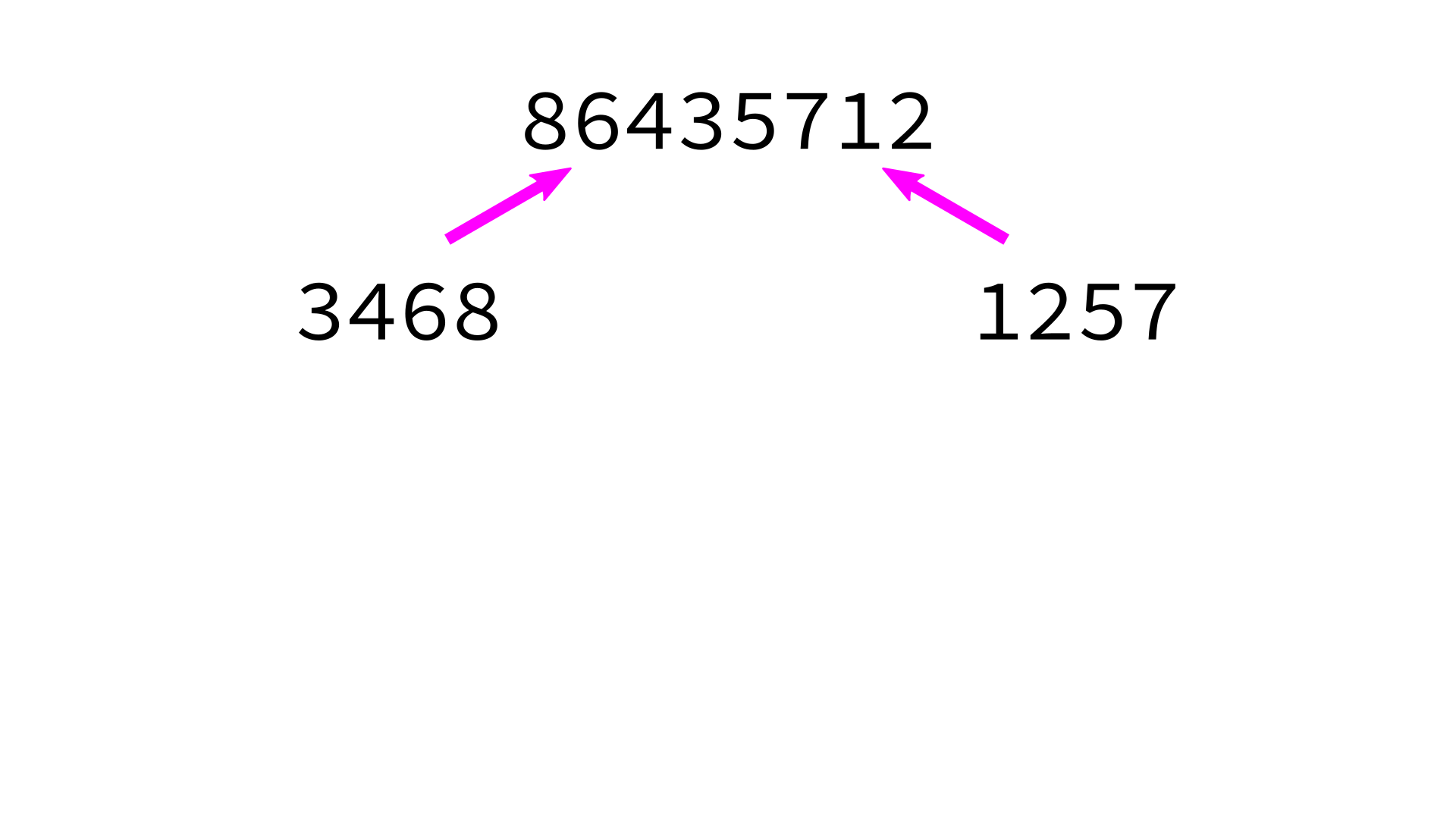
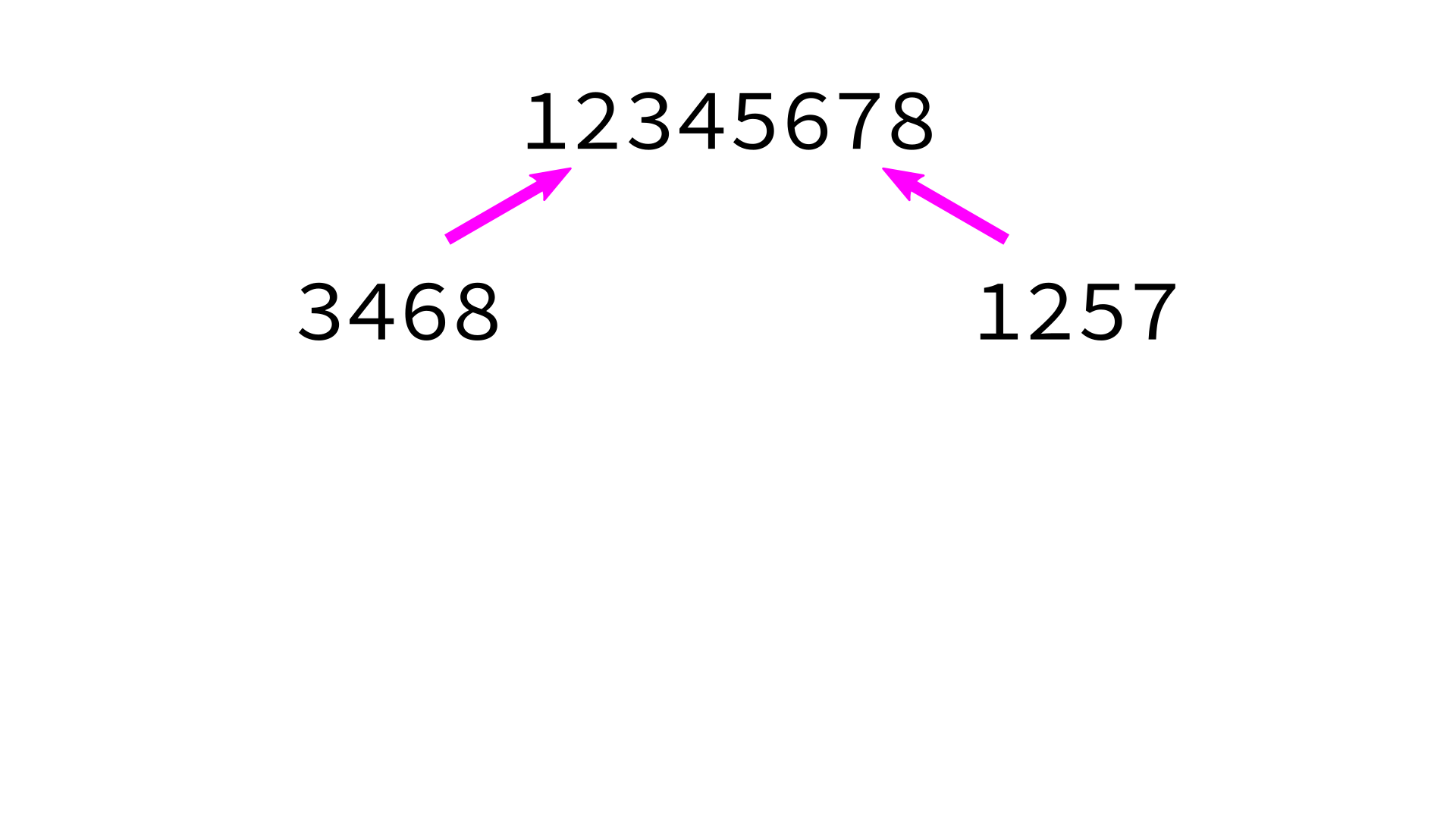

But how to merge?
This algorithm depends on having a function merge that can merge two sorted lists into a
single sorted list.
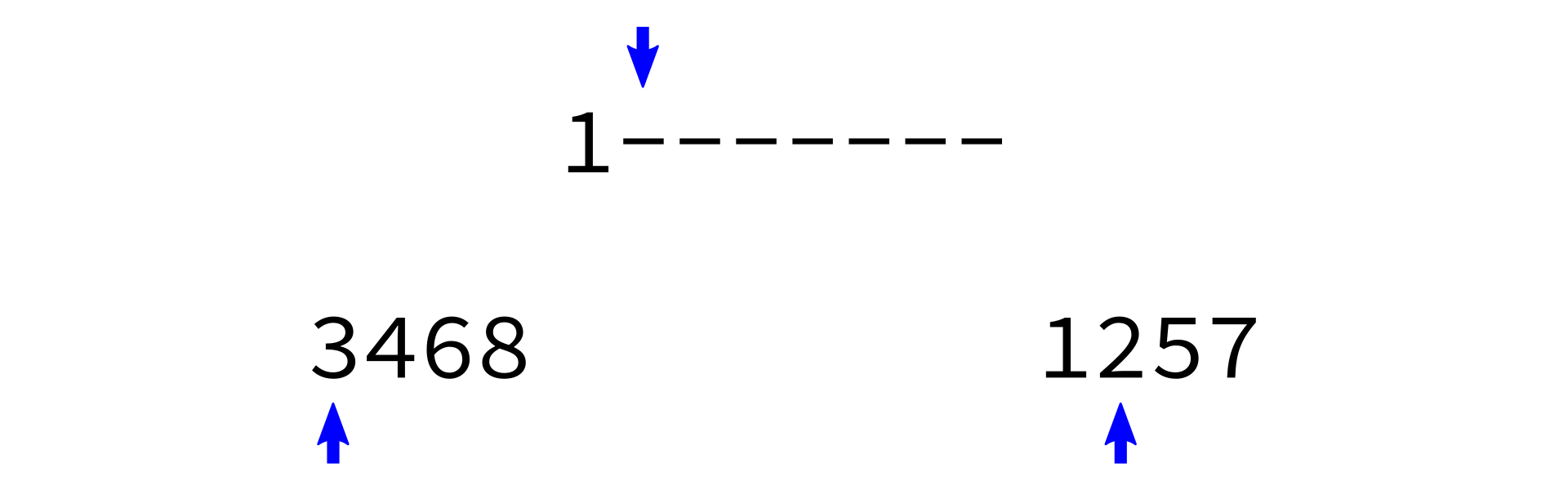
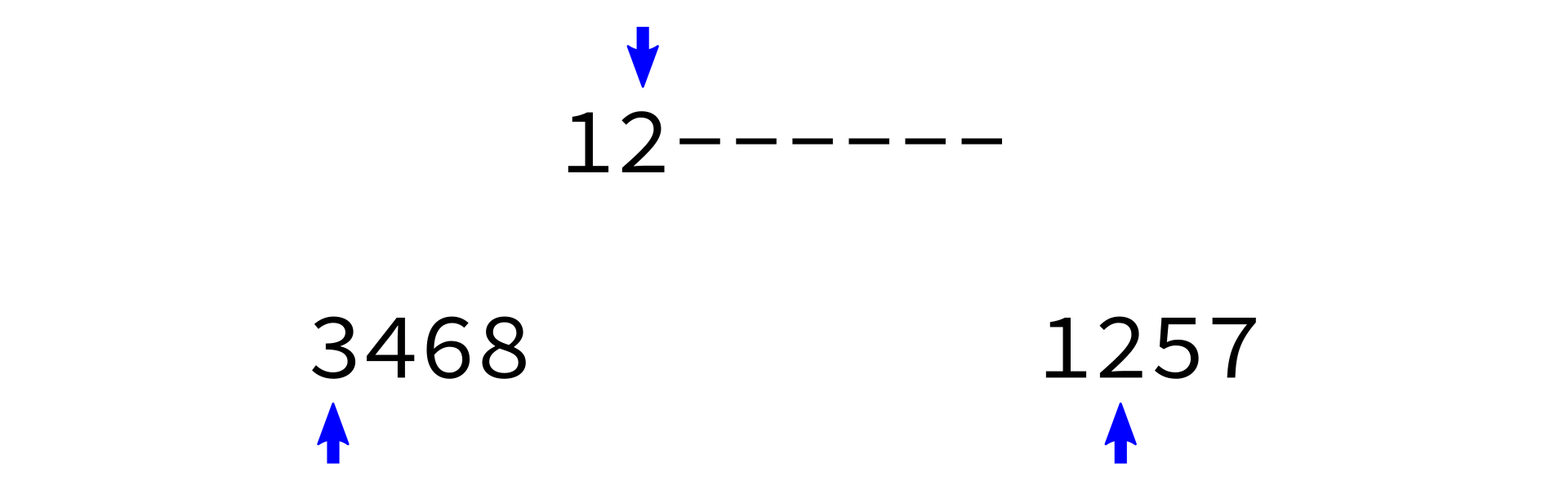
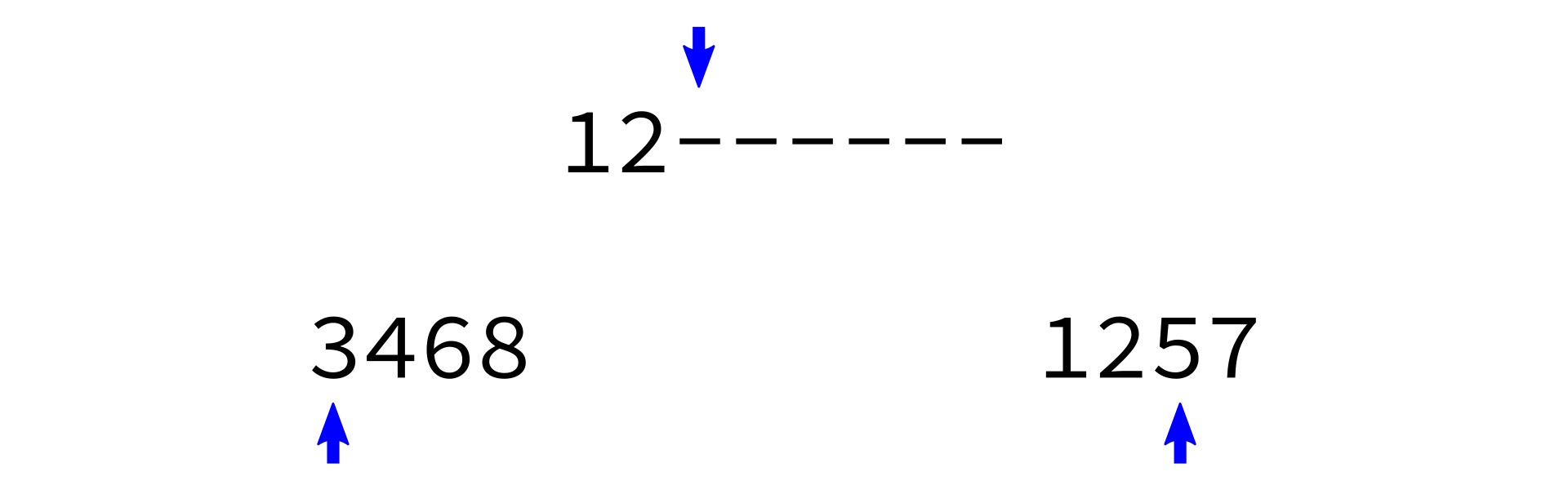
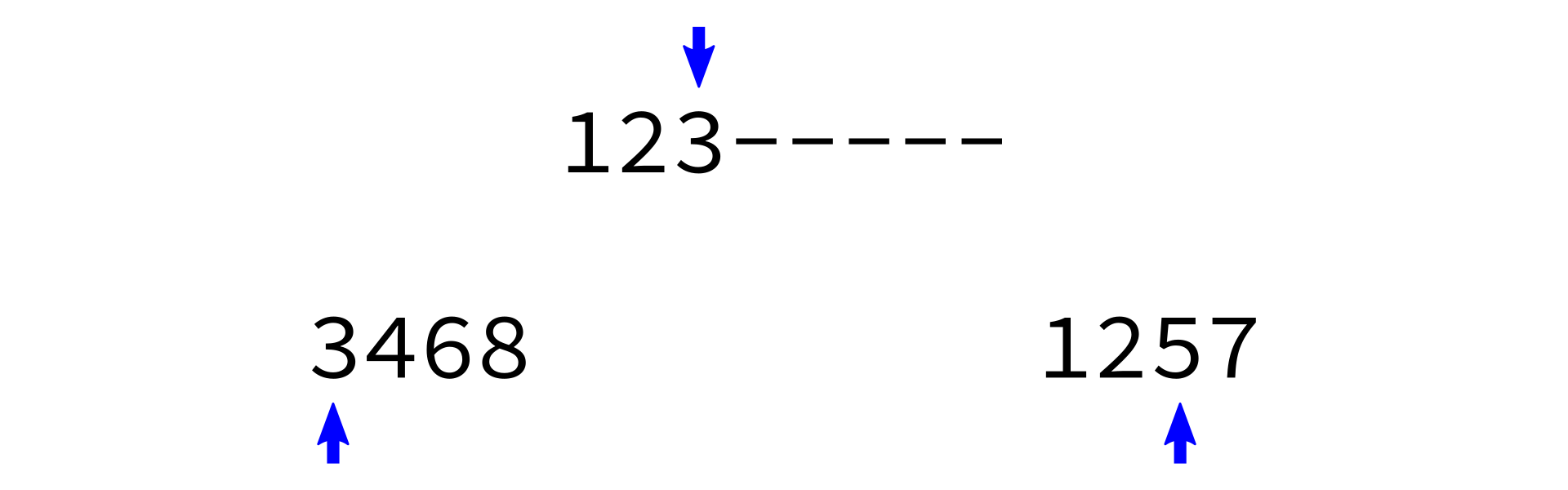
merge:
Input: sorted lists L0 and L1.
Goal: return a sorted list with same items as L0+L1
- Make a new empty list
L - Make integer variables
i0,i1to keep track of current position inL0,L1respectively. Set to zero. - While
i0 < len(L0)andi1 < len(L1), do the following:- Check which of
L0[i0]andL1[i1]is smaller. - Append the smaller one to
L. - Increment whichever one of
i0,i1was used.
- Check which of
- Append any remaining portion of
L0toL. - Append any remaining portion of
L1toL.
Merging sorted lists



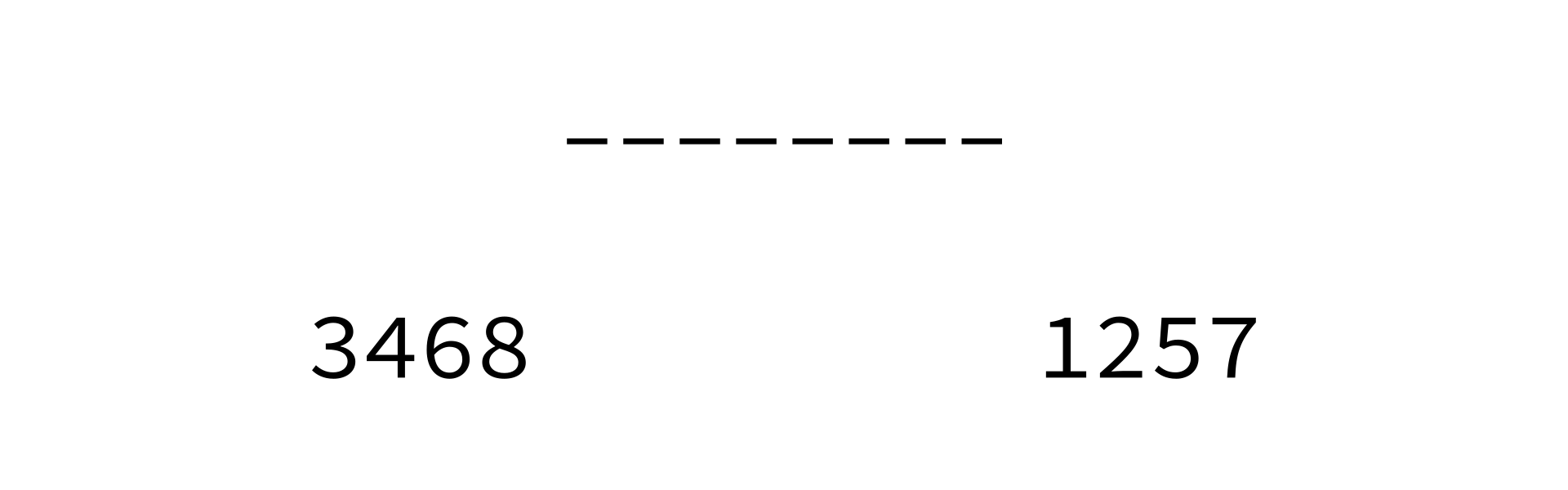
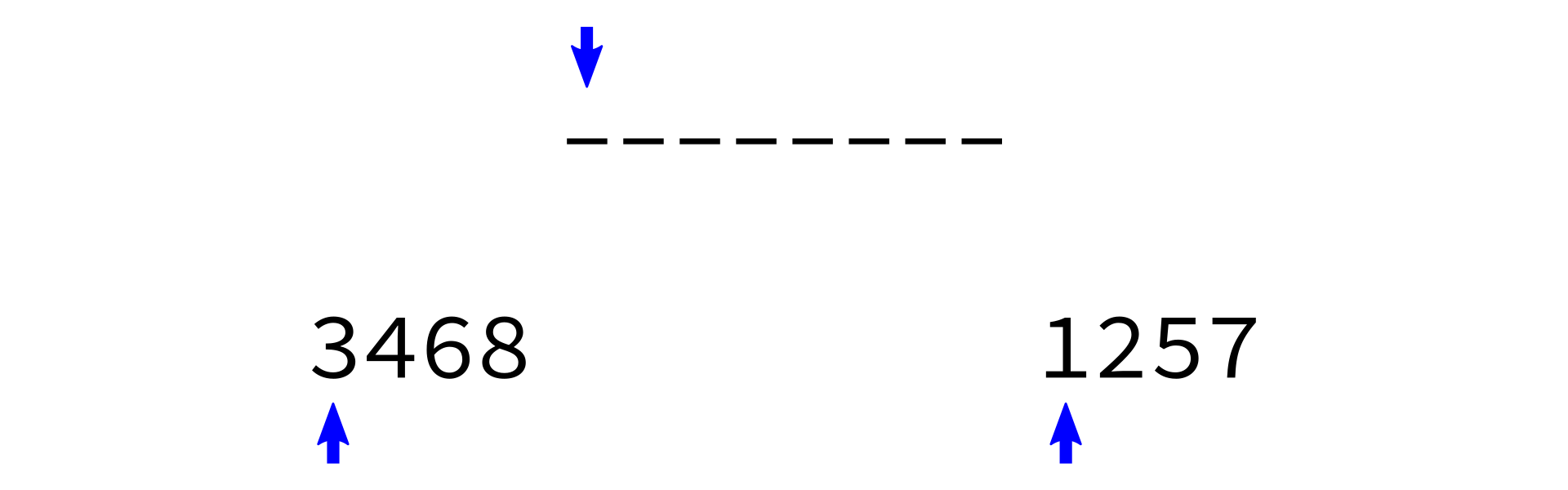
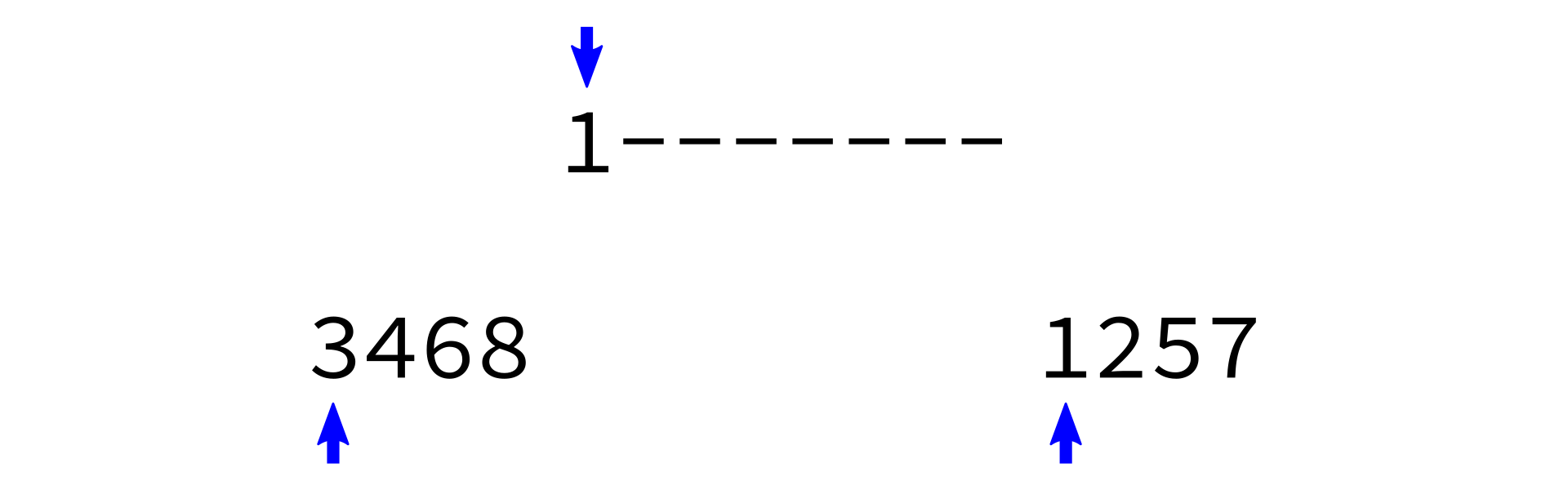
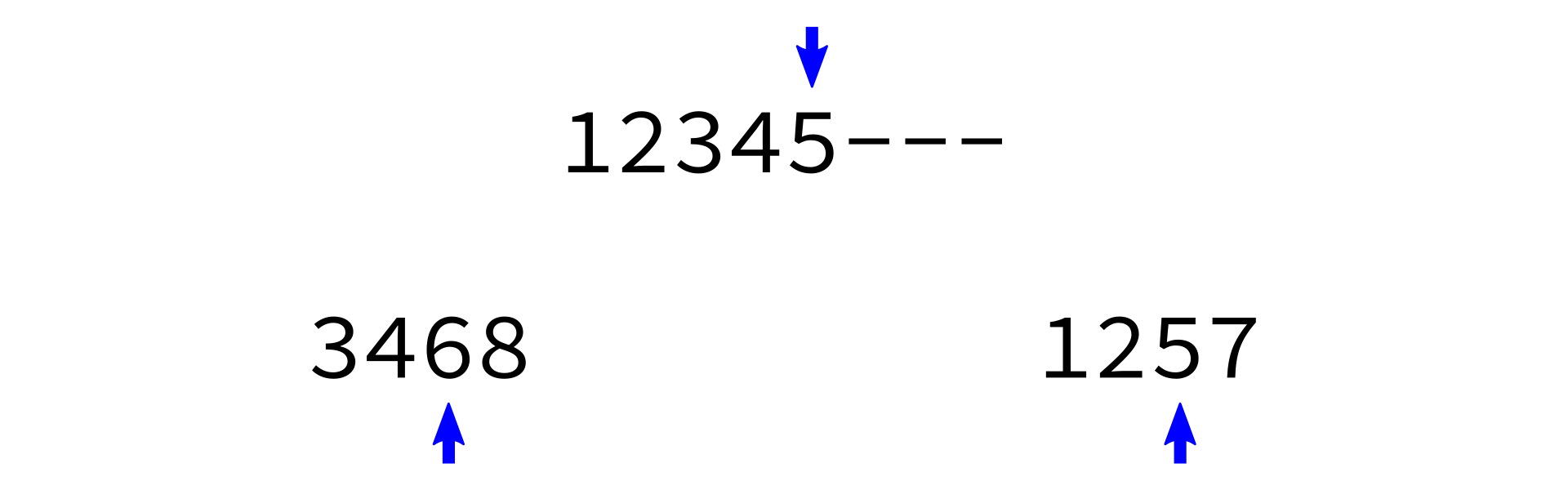









Coding time
Let's implement mergesort in Python.
References
- Recursion references from Lecture 9.
- Making nice visualizations of sorting algorithms is a cottage industry in CS education. Some you
might like to check out:
- 2D visualization through color sorting by Linus Lee
- Animated bar graph visualization of many sorting algorithms by Alex Macy
- Slanted line animated visualizations of mergesort and quicksort by Mike Bostock
- 2023-02-13 Finalization of the 2023 lecture this was based on
- 2024-02-05 Initial publication
- 2024-02-05 Reference link fixed
- 2024-02-06 Fix project 1 deadline